Downloadable of SSCP exam cost materials and free exam questions for ISC2 certification for consumer, Real Success Guaranteed with Updated SSCP pdf dumps vce Materials. 100% PASS System Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP) exam Today!
Also have SSCP free dumps questions for you:
NEW QUESTION 1
Which layer defines how packets are routed between end systems?
- A. Session layer
- B. Transport layer
- C. Network layer
- D. Data link layer
Answer: C
Explanation:
The network layer (layer 3) defines how packets are routed and relayed between end systems on the same network or on interconnected networks. Message routing, error detection and control of node traffic are managed at this level.
Reference(s) used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 82).
NEW QUESTION 2
When we encrypt or decrypt data there is a basic operation involving ones and zeros where they are compared in a process that looks something like this:
0101 0001 Plain text
0111 0011 Key stream
0010 0010 Output
What is this cryptographic operation called?
- A. Exclusive-OR
- B. Bit Swapping
- C. Logical-NOR
- D. Decryption
Answer: A
Explanation:
When we encrypt data we are basically taking the plaintext information and applying some key material or keystream and conducting something called an XOR or Exclusive-OR operation.
The symbol used for XOR is the following: This is a type of cipher known as a stream cipher.
The operation looks like this: 0101 0001 Plain text
0111 0011 Key stream
0010 0010 Output (ciphertext)
As you can see, it's not simple addition and the XOR Operation uses something called a truth table that explains why 0+1=1 and 1+1=0.
The rules are simples, if both bits are the same the result is zero, if both bits are not the same the result is one.
The following answers are incorrect:
- Bit Swapping: Incorrect. This isn't a known cryptographic operations.
- Logical NOR: Sorry, this isn't correct but is where only 0+0=1. All other combinations of 1+1, 1+0 equals 0. More on NOR here.
- Decryption: Sorry, this is the opposite of the process of encryption or, the process of applying the keystream to the plaintext to get the resulting encrypted text.
The following reference(s) was used to create this question:
For more details on XOR and all other QUESTION NO: s of cryptography. Subscribe to our holistic Security+ CBT tutorial at http://www.cccure.tv
and http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Exclusive-or and
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stream_cipher
NEW QUESTION 3
Controls to keep password sniffing attacks from compromising computer systems include which of the following?
- A. static and recurring passwords.
- B. encryption and recurring passwords.
- C. one-time passwords and encryption.
- D. static and one-time passwords.
Answer: C
Explanation:
To minimize the chance of passwords being captured one-time passwords would prevent a password sniffing attack because once used it is no longer valid. Encryption will also minimize these types of attacks.
The following answers are correct:
static and recurring passwords. This is incorrect because if there is no encryption then someone password sniffing would be able to capture the password much easier if it never changed.
encryption and recurring passwords. This is incorrect because while encryption helps, recurring passwords do nothing to minimize the risk of passwords being captured.
static and one-time passwords. This is incorrect because while one-time passwords will prevent these types of attacks, static passwords do nothing to minimize the risk of passwords being captured.
NEW QUESTION 4
Which device acting as a translator is used to connect two networks or applications from layer 4 up to layer 7 of the ISO/OSI Model?
- A. Bridge
- B. Repeater
- C. Router
- D. Gateway
Answer: D
Explanation:
A gateway is used to connect two networks using dissimilar protocols at the lower layers or it could also be at the highest level of the protocol stack.
Important Note:
For the purpose of the exam, you have to remember that a gateway is not synonymous to the term firewall.
The second thing you must remembers is the fact that a gateway act as a translation device.
It could be used to translate from IPX to TCP/IP for example. It could be used to convert different types of applications protocols and allow them to communicate together. A gateway could be at any of the OSI layers but usually tend to be higher up in the stack.
For your exam you should know the information below: Repeaters
A repeater provides the simplest type of connectivity, because it only repeats electrical
signals between cable segments, which enables it to extend a network. Repeaters work at the physical layer and are add-on devices for extending a network connection over a greater distance. The device amplifies signals because signals attenuate the farther they have to travel.
Repeaters can also work as line conditioners by actually cleaning up the signals. This works much better when amplifying digital signals than when amplifying analog signals,
because digital signals are discrete units, which makes extraction of background noise from them much easier for the amplifier. If the device is amplifying analog signals, any accompanying noise often is amplified as well, which may further distort the signal.
A hub is a multi-port repeater. A hub is often referred to as a concentrator because it is the physical communication device that allows several computers and devices to communicate with each other. A hub does not understand or work with IP or MAC addresses. When one system sends a signal to go to another system connected to it, the signal is broadcast to all the ports, and thus to all the systems connected to the concentrator.
Repeater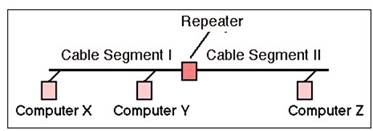
C:\Users\MCS\Desktop\1.jpg
Image Reference- http://www.erg.abdn.ac.uk/~gorry/course/images/repeater.gif Bridges
A bridge is a LAN device used to connect LAN segments. It works at the data link layer and therefore works with MAC addresses. A repeater does not work with addresses; it just forwards all signals it receives. When a frame arrives at a bridge, the bridge determines whether or not the MAC address is on the local network segment. If the MAC address is not on the local network segment, the bridge forwards the frame to the necessary network segment.
Bridge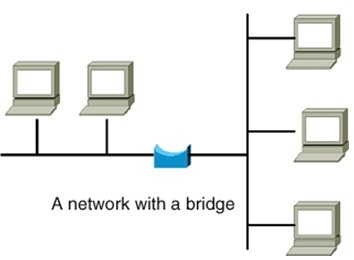
C:\Users\MCS\Desktop\1.jpg
Image Reference- http://www.oreillynet.com/network/2001/01/30/graphics/bridge.jpg Routers
Routers are layer 3, or network layer, devices that are used to connect similar or different networks. (For example, they can connect two Ethernet LANs or an Ethernet LAN to a Token Ring LAN.) A router is a device that has two or more interfaces and a routing table so it knows how to get packets to their destinations. It can filter traffic based on access control lists (ACLs), and it fragments packets when necessary. Because routers have more network-level knowledge, they can perform higher-level functions, such as calculating the shortest and most economical path between the sending and receiving hosts.
Router and Switch
C:\Users\MCS\Desktop\1.jpg
Image Reference- http://www.computer-networking-success.com/images/router-switch.jpg
Switches
Switches combine the functionality of a repeater and the functionality of a bridge. A switch amplifies the electrical signal, like a repeater, and has the built-in circuitry and intelligence of a bridge. It is a multi-port connection device that provides connections for individual computers or other hubs and switches.
Gateways
Gateway is a general term for software running on a device that connects two different environments and that many times acts as a translator for them or somehow restricts their interactions. Usually a gateway is needed when one environment speaks a different language, meaning it uses a certain protocol that the other environment does not understand. The gateway can translate Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX) protocol packets to IP packets, accept mail from one type of mail server and format it so another type of mail server can accept and understand it, or connect and translate different data link technologies such as FDDI to Ethernet.
Gateway Server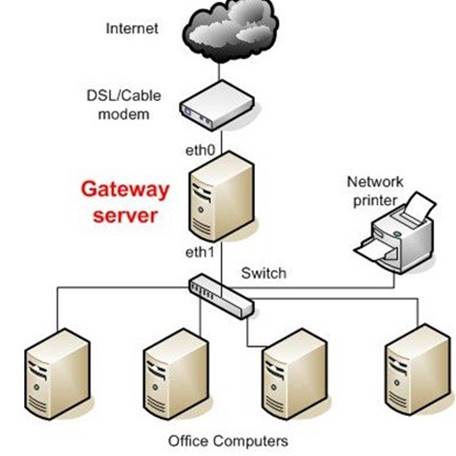
C:\Users\MCS\Desktop\1.jpg
Image Reference- http://static.howtoforge.com/images/screenshots/556af08d5e43aa768260f9e589dc547f- 3024.jpg
The following answers are incorrect:
Repeater - A repeater provides the simplest type of connectivity, because it only repeats electrical signals between cable segments, which enables it to extend a network. Repeaters work at the physical layer and are add-on devices for extending a network connection over a greater distance. The device amplifies signals because signals attenuate the farther they have to travel.
Bridges - A bridge is a LAN device used to connect LAN segments. It works at the data link layer and therefore works with MAC addresses. A repeater does not work with addresses; it just forwards all signals it receives. When a frame arrives at a bridge, the bridge determines whether or not the MAC address is on the local network segment. If the MAC
address is not on the local network segment, the bridge forwards the frame to the necessary network segment.
Routers - Routers are layer 3, or network layer, devices that are used to connect similar or different networks. (For example, they can connect two Ethernet LANs or an Ethernet LAN to a Token Ring LAN.) A router is a device that has two or more interfaces and a routing table so it knows how to get packets to their destinations. It can filter traffic based on access control lists (ACLs), and it fragments packets when necessary.
Following reference(s) were/was used to create this question: CISA review manual 2014 Page number 263
Official ISC2 guide to CISSP CBK 3rd Edition Page number 229 and 230
NEW QUESTION 5
Which layer of the TCP/IP protocol stack corresponds to the ISO/OSI Network layer (layer 3)?
- A. Host-to-host layer
- B. Internet layer
- C. Network access layer
- D. Session layer
Answer: B
Explanation:
The Internet layer in the TCP/IP protocol stack corresponds to the network layer (layer 3) in the OSI/ISO model. The host-to-host layer corresponds to the transport layer (layer 4) in the OSI/ISO model. The Network access layer corresponds to the data link and physical layers (layers 2 and 1) in the OSI/ISO model. The session layer is not defined in the TCP/IP protocol stack.
Source: WALLHOFF, John, CBK#2 Telecommunications and Network Security (CISSP Study Guide), April 2002 (page 1).
NEW QUESTION 6
Controls provide accountability for individuals who are accessing sensitive information. This accountability is accomplished:
- A. through access control mechanisms that require identification and authentication and through the audit function.
- B. through logical or technical controls involving the restriction of access to systems and the protection of information.
- C. through logical or technical controls but not involving the restriction of access to systems and the protection of information.
- D. through access control mechanisms that do not require identification and authentication and do not operate through the audit function.
Answer: A
Explanation:
Controls provide accountability for individuals who are accessing sensitive information. This accountability is accomplished through access control mechanisms that require identification and authentication and through the audit function. These controls must be in accordance with and accurately represent the organization's security policy. Assurance procedures ensure that the control mechanisms correctly implement the security policy for the entire life cycle of an information system.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 33.
NEW QUESTION 7
An attack initiated by an entity that is authorized to access system resources but uses them in a way not approved by those who granted the authorization is known as a(n):
- A. active attack
- B. outside attack
- C. inside attack
- D. passive attack
Answer: C
Explanation:
An inside attack is an attack initiated by an entity inside the security perimeter, an entity that is authorized to access system resources but uses them in a way not approved by those who granted the authorization whereas an outside attack is initiated from outside the perimeter, by an unauthorized or illegitimate user of the system. An active attack attempts to alter system resources to affect their operation and a passive attack attempts to learn or make use of the information from the system but does not affect system resources.
Source: SHIREY, Robert W., RFC2828: Internet Security Glossary, may 2000.
NEW QUESTION 8
Remote Procedure Call (RPC) is a protocol that one program can use to request a service from a program located in another computer in a network. Within which OSI/ISO layer is RPC implemented?
- A. Session layer
- B. Transport layer
- C. Data link layer
- D. Network layer
Answer: A
Explanation:
The Answer Session layer, which establishes, maintains and manages sessions and synchronization of data flow. Session layer protocols control application-to- application communications, which is what an RPC call is.
The following answers are incorrect:
Transport layer: The Transport layer handles computer-to computer communications, rather than application-to-application communications like RPC.
Data link Layer: The Data Link layer protocols can be divided into either Logical Link
Control (LLC) or Media Access Control (MAC) sublayers. Protocols like SLIP, PPP, RARP and L2TP are at this layer. An application-to-application protocol like RPC would not be addressed at this layer.
Network layer: The Network Layer is mostly concerned with routing and addressing of information, not application-to-application communication calls such as an RPC call.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
The Remote Procedure Call (RPC) protocol is implemented at the Session layer, which establishes, maintains and manages sessions as well as synchronization of the data flow. Source: Jason Robinett's CISSP Cram Sheet: domain2.
Source: Shon Harris AIO v3 pg. 423
NEW QUESTION 9
Devices that supply power when the commercial utility power system fails are called which of the following?
- A. power conditioners
- B. uninterruptible power supplies
- C. power filters
- D. power dividers
Answer: B
Explanation:
From Shon Harris AIO Fifth Edition:
Protecting power can be done in three ways: through UPSs, power line conditioners, and backup sources.
UPSs use battery packs that range in size and capacity. A UPS can be online or standby. Online UPS systems use AC line voltage to charge a bank of batteries. When in use, the
UPS has an inverter that changes the DC output from the batteries into the required AC
form and that regulates the voltage as it powers computer devices.
Online UPS systems have the normal primary power passing through them day in and day out. They constantly provide power from their own inverters, even when the electric power is in proper use. Since the environment's electricity passes through this type of UPS all the time, the UPS device is able to quickly detect when a power failure takes place. An online UPS can provide the necessary electricity and picks up the load after a power failure much more quickly than a standby UPS.
Standby UPS devices stay inactive until a power line fails. The system has sensors that detect a power failure, and the load is switched to the battery pack. The switch to the battery pack is what causes the small delay in electricity being provided.
So an online UPS picks up the load much more quickly than a standby UPS, but costs more of course.
NEW QUESTION 10
In the UTP category rating, the tighter the wind:
- A. the higher the rating and its resistance against interference and crosstalk.
- B. the slower the rating and its resistance against interference and attenuation.
- C. the shorter the rating and its resistance against interference and attenuation.
- D. the longer the rating and its resistance against interference and attenuation.
Answer: A
Explanation:
The category rating is based on how tightly the copper cable is wound within
the shielding: The tighter the wind, the higher the rating and its resistance against interference and crosstalk.
Twisted pair copper cabling is a form of wiring in which two conductors are wound together for the purposes of canceling out electromagnetic interference (EMI) from external sources and crosstalk from neighboring wires. Twisting wires decreases interference because the loop area between the wires (which determines the magnetic coupling into the signal) is reduced. In balanced pair operation, the two wires typically carry equal and opposite signals (differential mode) which are combined by subtraction at the destination. The noise from the two wires cancel each other in this subtraction because the two wires have been exposed to similar EMI.
The twist rate (usually defined in twists per metre) makes up part of the specification for a given type of cable. The greater the number of twists, the greater the attenuation of crosstalk. Where pairs are not twisted, as in most residential interior telephone wiring, one member of the pair may be closer to the source than the other, and thus exposed to slightly different induced EMF.
Reference:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 101.
and
http://www.consultants-online.co.za/pub/itap_101/html/ch04s05.html
NEW QUESTION 11
Which of the following is NOT a task normally performed by a Computer Incident Response Team (CIRT)?
- A. Develop an information security policy.
- B. Coordinate the distribution of information pertaining to the incident to the appropriate parties.
- C. Mitigate risk to the enterprise.
- D. Assemble teams to investigate the potential vulnerabilities.
Answer: A
Explanation:
Writing a corporate security policy is normally a task of upper management in an organization. Other tasks would usually be performed by a Computer Incident Response Team.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 64).
NEW QUESTION 12
What is called an attack where the attacker spoofs the source IP address in an ICMP ECHO broadcast packet so it seems to have originated at the victim's system, in order to flood it with REPLY packets?
- A. SYN Flood attack
- B. Smurf attack
- C. Ping of Death attack
- D. Denial of Service (DOS) attack
Answer: B
Explanation:
Although it may cause a denial of service to the victim's system, this type of attack is a Smurf attack. A SYN Flood attack uses up all of a system's resources by setting up a number of bogus communication sockets on the victim's system. A Ping of Death attack is done by sending IP packets that exceed the maximum legal length (65535 octets). Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw- Hill/Osborne, 2002, chapter 11: Application and System Development (page 789).
NEW QUESTION 13
What is a characteristic of using the Electronic Code Book mode of DES encryption?
- A. A given block of plaintext and a given key will always produce the same ciphertext.
- B. Repetitive encryption obscures any repeated patterns that may have been present in the plaintext.
- C. Individual characters are encoded by combining output from earlier encryption routines with plaintext.
- D. The previous DES output is used as input.
Answer: A
Explanation:
A given message and key always produce the same ciphertext. The following answers are incorrect:
Repetitive encryption obscures any repeated patterns that may have been present in the plaintext. Is incorrect because with Electronic Code Book a given 64 bit block of plaintext always produces the same ciphertext
Individual characters are encoded by combining output from earlier encryption routines with plaintext. This is incorrect because with Electronic Code Book processing 64 bits at a time until the end of the file was reached. This is a characteristic of Cipher Feedback. Cipher Feedback the ciphertext is run through a key-generating device to create the key for the next block of plaintext.
The previous DES output is used as input. Is incorrect because This is incorrect because with Electronic Code Book processing 64 bits at a time until the end of the file was reached
. This is a characteristic of Cipher Block Chaining. Cipher Block Chaining uses the output from the previous block to encrypt the next block.
NEW QUESTION 14
Failure of a contingency plan is usually:
- A. A technical failure.
- B. A management failure.
- C. Because of a lack of awareness.
- D. Because of a lack of training.
Answer: B
Explanation:
Failure of a contingency plan is usually management failure to exhibit ongoing interest and concern about the BCP/DRP effort, and to provide financial and other resources as needed. Lack of management support will result in a lack awareness and training.
Source: ANDRESS, Mandy, Exam Cram CISSP, Coriolis, 2001, Chapter 9: Business Continuity Planning (BCP) and Disaster Recovery Planning (DRP) (page 163).
NEW QUESTION 15
Which of the following standards is concerned with message handling?
- A. X.400
- B. X.500
- C. X.509
- D. X.800
Answer: A
Explanation:
X.400 is used in e-mail as a message handling protocol. X.500 is used in directory services. X.509 is used in digital certificates and X.800 is used a network security standard.
Reference: http://www.alvestrand.no/x400/.
NEW QUESTION 16
Which of the following statements pertaining to protection rings is false?
- A. They provide strict boundaries and definitions on what the processes that work within each ring can access.
- B. Programs operating in inner rings are usually referred to as existing in a privileged mode.
- C. They support the CIA triad requirements of multitasking operating systems.
- D. They provide users with a direct access to peripherals
Answer: D
Explanation:
In computer science, hierarchical protection domains, often called protection rings, are mechanisms to protect data and functionality from faults (fault tolerance) and malicious behaviour (computer security). This approach is diametrically opposite to that of capability-based security.
Computer operating systems provide different levels of access to resources. A protection ring is one of two or more hierarchical levels or layers of privilege within the architecture of a computer system. This is generally hardware-enforced by some CPU architectures that provide different CPU modes at the hardware or microcode level.
Rings are arranged in a hierarchy from most privileged (most trusted, usually numbered zero) to least privileged (least trusted, usually with the highest ring number). On most operating systems, Ring 0 is the level with the most privileges and interacts most directly with the physical hardware such as the CPU and memory.
Special gates between rings are provided to allow an outer ring to access an inner ring's resources in a predefined manner, as opposed to allowing arbitrary usage. Correctly gating access between rings can improve security by preventing programs from one ring or privilege level from misusing resources intended for programs in another. For example,
spyware running as a user program in Ring 3 should be prevented from turning on a web camera without informing the user, since hardware access should be a Ring 1 function reserved for device drivers. Programs such as web browsers running in higher numbered rings must request access to the network, a resource restricted to a lower numbered ring.
"They provide strict boundaries and definitions on what the processes that work within each ring can access" is incorrect. This is in fact one of the characteristics of a ring protection system.
"Programs operating in inner rings are usually referred to as existing in a privileged mode" is incorrect. This is in fact one of the characteristics of a ring protection system.
"They support the CIA triad requirements of multitasking operating systems" is incorrect. This is in fact one of the characteristics of a ring protection system.
Reference(s) used for this question: CBK, pp. 310-311
AIO3, pp. 253-256
AIOv4 Security Architecture and Design (pages 308 - 310) AIOv5 Security Architecture and Design (pages 309 - 312)
NEW QUESTION 17
What are called user interfaces that limit the functions that can be selected by a user?
- A. Constrained user interfaces
- B. Limited user interfaces
- C. Mini user interfaces
- D. Unlimited user interfaces
Answer: A
Explanation:
Constrained user interfaces limit the functions that can be selected by a user.
Another method for controlling access is by restricting users to specific functions based on their role in the system. This is typically implemented by limiting available menus, data views, encryption, or by physically constraining the user interfaces.
This is common on devices such as an automated teller machine (ATM). The advantage of a constrained user interface is that it limits potential avenues of attack and system failure by restricting the processing options that are available to the user.
On an ATM machine, if a user does not have a checking account with the bank he or she will not be shown the ??Withdraw money from checking?? option. Likewise, an information system might have an ??Add/Remove Users?? menu option for administrators, but if a normal, non-administrative user logs in he or she will not even see that menu option. By not even identifying potential options for non-qualifying users, the system limits the potentially harmful execution of unauthorized system or application commands.
Many database management systems have the concept of ??views.?? A database view is an extract of the data stored in the database that is filtered based on predefined user or system criteria. This permits multiple users to access the same database while only having the ability to access data they need (or are allowed to have) and not data for another user. The use of database views is another example of a constrained user interface.
The following were incorrect answers:
All of the other choices presented were bogus answers.
The following reference(s) were used for this question:
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 1989-2002). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
NEW QUESTION 18
Packet Filtering Firewalls can also enable access for:
- A. only authorized application port or service numbers.
- B. only unauthorized application port or service numbers.
- C. only authorized application port or ex-service numbers.
- D. only authorized application port or service integers.
Answer: A
Explanation:
Firewall rules can be used to enable access for traffic to specific ports or services. "Service numbers" is rather stilted English but you may encounter these types of wordings on the actual exam -- don't let them confuse you.
"Only unauthorized application port or service numbers" is incorrect. Unauthorized ports/services would be blocked in a properly installed firewall rather than permitting access.
"Only authorized application port or ex-service numbers" is incorrect. "Ex-service" numbers is a nonsense term meant to distract you.
"Only authorized application port or service integers." While service numbers are in fact integers, the more usual (and therefore better) answer is either service or "service number."
References CBK, p. 464
AIO3, pp. 482 ?C 484
NEW QUESTION 19
Which SSL version offers client-side authentication?
- A. SSL v1
- B. SSL v2
- C. SSL v3
- D. SSL v4
Answer: C
Explanation:
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is the technology used in most Web-based applications. SSL version 2.0 supports strong authentication of the web server, but the authentication of the client side only comes with version 3.0. SSL v4 is not a defined standard.
Source: TIPTON, Harold F. & KRAUSE, Micki, Information Security Management Handbook, 4th edition (volume 1), 2000, CRC Press, Chapter 3, Secured Connections to External Networks (page 54).
NEW QUESTION 20
The number of violations that will be accepted or forgiven before a violation record is produced is called which of the following?
- A. clipping level
- B. acceptance level
- C. forgiveness level
- D. logging level
Answer: A
Explanation:
The correct answer is "clipping level". This is the point at which a system decides to take some sort of action when an action repeats a preset number of times. That action may be to log the activity, lock a user account, temporarily close a port, etc.
Example: The most classic example of a clipping level is failed login attempts. If you have a system configured to lock a user's account after three failed login attemts, that is the "clipping level".
The other answers are not correct because:
Acceptance level, forgiveness level, and logging level are nonsensical terms that do not exist (to my knowledge) within network security.
Reference:
Official ISC2 Guide - The term "clipping level" is not in the glossary or index of that book. I cannot find it in the text either. However, I'm quite certain that it would be considered part of the CBK, despite its exclusion from the Official Guide.
All in One Third Edition page: 136 - 137
NEW QUESTION 21
Which of the following statements pertaining to disaster recovery planning is incorrect?
- A. Every organization must have a disaster recovery plan
- B. A disaster recovery plan contains actions to be taken before, during and after a disruptive event.
- C. The major goal of disaster recovery planning is to provide an organized way to make decisions if a disruptive event occurs.
- D. A disaster recovery plan should cover return from alternate facilities to primary facilities.
Answer: A
Explanation:
It is possible that an organization may not need a disaster recovery plan. An organization may not have any critical processing areas or system and they would be able to withstand lengthy interruptions.
Remember that DRP is related to systems needed to support your most critical business functions.
The DRP plan covers actions to be taken when a disaster occur but DRP PLANNING which is the keywork in the question would also include steps that happen before you use the plan such as development of the plan, training, drills, logistics, and a lot more.
To be effective, the plan would certainly cover before, during, and after the disaster actions.
It may take you a couple years to develop a plan for a medium size company, there is a lot that has to happen before the plan would be actually used in a real disaster scenario. Plan for the worst and hope for the best.
All other statements are true. NOTE FROM CLEMENT:
Below is a great article on who legally needs a plan which is very much in line with this
question. Does EVERY company needs a plan? The legal answer is NO. Some companies, industries, will be required according to laws or regulations to have a plan. A blank statement saying: All companies MUST have a plan would not be accurate. The article below is specific to the USA but similar laws will exist in many other countries.
Some companies such as utilities, power, etc... might also need plan if they have been defined as Critical Infrastructure by the government. The legal side of IT is always very complex and varies in different countries. Always talk to your lawyer to ensure you follow the law of the land :-)
Read the details below:
So Who, Legally, MUST Plan?
With the caveats above, let??s cover a few of the common laws where there is a duty to have a disaster recovery plan. I will try to include the basis for that requirement, where there is an implied mandate to do so, and what the difference is between the two
Banks and Financial Institutions MUST Have a Plan
The Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (Council) was established on March 10, 1979, pursuant to Title X of the Financial Institutions Regulatory and Interest Rate Control Act of 1978 (FIRA), Public Law 95-630. In 1989, Title XI of the Financial Institutions Reform, Recovery and Enforcement Act of 1989 (FIRREA) established the Examination Council (the Council).
The Council is a formal interagency body empowered to prescribe uniform principles, standards, and report forms for the federal examination of financial institutions by the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (FRB), the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), the National Credit Union Administration (NCUA), the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), and the Office of Thrift Supervision (OTS); and to make recommendations to promote uniformity in the supervision of financial institutions. In other words, every bank, savings and loan, credit union, and other financial institution is governed by the principles adopted by the Council.
In March of 2003, the Council released its Business Continuity Planning handbook designed to provide guidance and examination procedures for examiners in evaluating financial institution and service provider risk-management processes.
Stockbrokers MUST Have a Plan
The National Association of Securities Dealers (NASD) has adopted rules that require all its members to have business continuity plans. The NASD oversees the activities of more than 5,100 brokerage firms, approximately 130,800 branch offices and more than 658,770 registered securities representatives.
As of June 14, 2004, the rules apply to all NASD member firms. The requirements, which are specified in Rule 3510, begin with the following:
3510. Business Continuity Plans. (a) Each member must create and maintain a written business continuity plan identifying procedures relating to an emergency or significant business disruption. Such procedures must be reasonably designed to enable the member
to meet its existing obligations to customers. In addition, such procedures must address the member??s existing relationships with other broker-dealers and counter-parties. The business continuity plan must be made available promptly upon request to NASD staff.
NOTE:
The rules apply to every company that deals in securities, such as brokers, dealers, and their representatives, it does NOT apply to the listed companies themselves.
Electric Utilities WILL Need a Plan
The disaster recovery function relating to the electric utility grid is presently undergoing a change. Prior to 2005, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) could only coordinate volunteer efforts between utilities. This has changed with the adoption of Title XII of the Energy Policy Act of 2005 (16 U.S.C. 824o). That new law authorizes the FERC to create an Electric Reliability Organization (ERO).
The ERO will have the capability to adopt and enforce reliability standards for "all users, owners, and operators of the bulk power system" in the United States. At this time, FERC is in the process of finalizing the rules for the creation of the ERO. Once the ERO is created, it will begin the process of establishing reliability standards.
It is very safe to assume that the ERO will adopt standards for service restoration and disaster recovery, particularly after such widespread disasters as Hurricane Katrina. Telecommunications Utilities SHOULD Have Plans, but MIGHT NOT
Telecommunications utilities are governed on the federal level by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) for interstate services and by state Public Utility Commissions (PUCs) for services within the state.
The FCC has created the Network Reliability and Interoperability Council (NRIC). The role of the NRIC is to develop recommendations for the FCC and the telecommunications industry to "insure [sic] optimal reliability, security, interoperability and interconnectivity of, and accessibility to, public communications networks and the internet." The NRIC members are senior representatives of providers and users of telecommunications services and products, including telecommunications carriers, the satellite, cable television, wireless and computer industries, trade associations, labor and consumer representatives, manufacturers, research organizations, and government-related organizations.
There is no explicit provision that we could find that says telecommunications carriers must have a Disaster Recovery Plan. As I have stated frequently in this series of articles on disaster recovery, however, telecommunications facilities are tempting targets for terrorism. I have not changed my mind in that regard and urge caution.
You might also want to consider what the liability of a telephone company is if it does have a disaster that causes loss to your organization. In three words: It??s not much. The following is the statement used in most telephone company tariffs with regard to its liability:
The Telephone Company??s liability, if any, for its gross negligence or willful misconduct is not limited by this tariff. With respect to any other claim or suit, by a customer or any others, for damages arising out of mistakes, omissions, interruptions, delays or errors, or defects in transmission occurring in the course of furnishing services hereunder, the Telephone Company??s liability, if any, shall not exceed an amount equivalent to the proportionate charge to the customer for the period of service during which such mistake, omission, interruption, delay, error or defect in transmission or service occurs and continues. (Source, General Exchange Tariff for major carrier)
All Health Care Providers WILL Need a Disaster Recovery Plan
HIPAA is an acronym for the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, Public Law 104-191, which amended the Internal Revenue Service Code of 1986. Also known as the Kennedy-Kassebaum Act, the Act includes a section, Title II, entitled Administrative Simplification, requiring "Improved efficiency in healthcare delivery by standardizing electronic data interchange, and protection of confidentiality and security of health data through setting and enforcing standards."
The legislation called upon the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) to publish new rules that will ensure security standards protecting the confidentiality and integrity of "individually identifiable health information," past, present, or future.
The final Security Rule was published by HHS on February 20, 2003 and provides for a uniform level of protection of all health information that is housed or transmitted electronically and that pertains to an individual.
The Security Rule requires covered entities to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of all electronic protected health information (ePHI) that the covered entity creates, receives, maintains, or transmits. It also requires entities to protect against any reasonably anticipated threats or hazards to the security or integrity of ePHI, protect against any reasonably anticipated uses or disclosures of such information that are not permitted or required by the Privacy Rule, and ensure compliance by their workforce.
Required safeguards include application of appropriate policies and procedures, safeguarding physical access to ePHI, and ensuring that technical security measures are in place to protect networks, computers and other electronic devices.
Companies with More than 10 Employees
The United States Department of Labor has adopted numerous rules and regulations in regard to workplace safety as part of the Occupational Safety and Health Act. For example, 29 USC 654 specifically requires:
(a) Each employer:
(1) shall furnish to each of his employees employment and a place of employment which are free from recognized hazards that are causing or are likely to cause death or serious physical harm to his employees;
(2) shall comply with occupational safety and health standards promulgated under this Act.
(b) Each employee shall comply with occupational safety and health standards and all rules, regulations, and orders issued pursuant to this Act which are applicable to his own actions and conduct.
Other Considerations or Expensive Research QUESTION NO: s for Lawyers (Sorry, Eddie!)
The Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977
Internal Revenue Service (IRS) Law for Protecting Taxpayer Information Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Mandated Requirements Homeland Security and Terrorist Prevention
Pandemic (Bird Flu) Prevention ISO 9000 Certification
Requirements for Radio and TV Broadcasters Contract Obligations to Customers
Document Protection and Retention Laws Personal Identity Theft...and MORE!
Suffice it to say you will need to check with your legal department for specific requirements in your business and industry!
I would like to thank my good friend, Eddie M. Pope, for his insightful contributions to this article, our upcoming book, and my ever-growing pool of lawyer jokes. If you want more information on the legal aspects of recovery planning, Eddie can be contacted at my company or via email at mailto:mempope@tellawcomlabs.com. (Eddie cannot, of course, give you legal advice, but he can point you in the right direction.)
I hope this article helps you better understand the complex realities of the legal reasons why we plan and wish you the best of luck
See original article at: http://www.informit.com/articles/article.aspx?p=777896 See another interesting article on the subject at:
http://www.informit.com/articles/article.aspx?p=677910&seqNum=1
References used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 8: Business Continuity Planning and Disaster Recovery Planning (page 281).
NEW QUESTION 22
What uses a key of the same length as the message where each bit or character from the plaintext is encrypted by a modular addition?
- A. Running key cipher
- B. One-time pad
- C. Steganography
- D. Cipher block chaining
Answer: B
Explanation:
In cryptography, the one-time pad (OTP) is a type of encryption that is impossible to crack if used correctly. Each bit or character from the plaintext is encrypted by a modular addition with a bit or character from a secret random key (or pad) of the same length as the plaintext, resulting in a ciphertext. If the key is truly random, at least as long as the plaintext, never reused in whole or part, and kept secret, the ciphertext will be impossible to decrypt or break without knowing the key. It has also been proven that any cipher with the perfect secrecy property must use keys with effectively the same requirements as OTP keys. However, practical problems have prevented one-time pads from being widely used.
First described by Frank Miller in 1882, the one-time pad was re-invented in 1917 and patented a couple of years later. It is derived from the Vernam cipher, named after Gilbert Vernam, one of its inventors. Vernam's system was a cipher that combined a message with a key read from a punched tape. In its original form, Vernam's system was vulnerable because the key tape was a loop, which was reused whenever the loop made a full cycle. One-time use came a little later when Joseph Mauborgne recognized that if the key tape were totally random, cryptanalysis would be impossible.
The "pad" part of the name comes from early implementations where the key material was distributed as a pad of paper, so the top sheet could be easily torn off and destroyed after use. For easy concealment, the pad was sometimes reduced to such a small size that a powerful magnifying glass was required to use it. Photos show captured KGB pads that fit in the palm of one's hand, or in a walnut shell. To increase security, one-time pads were sometimes printed onto sheets of highly flammable nitrocellulose so they could be quickly burned.
The following are incorrect answers:
A running key cipher uses articles in the physical world rather than an electronic algorithm. In classical cryptography, the running key cipher is a type of polyalphabetic substitution cipher in which a text, typically from a book, is used to provide a very long keystream. Usually, the book to be used would be agreed ahead of time, while the passage to use would be chosen randomly for each message and secretly indicated somewhere in the message.
The Running Key cipher has the same internal workings as the Vigenere cipher. The difference lies in how the key is chosen; the Vigenere cipher uses a short key that repeats, whereas the running key cipher uses a long key such as an excerpt from a book. This means the key does not repeat, making cryptanalysis more difficult. The cipher can still be broken though, as there are statistical patterns in both the key and the plaintext which can be exploited.
Steganography is a method where the very existence of the message is concealed. It is the art and science of encoding hidden messages in such a way that no one, apart from the sender and intended recipient, suspects the existence of the message. it is sometimes referred to as Hiding in Plain Sight.
Cipher block chaining is a DES operating mode. IBM invented the cipher-block chaining (CBC) mode of operation in 1976. In CBC mode, each block of plaintext is XORed with the previous ciphertext block before being encrypted. This way, each ciphertext block depends on all plaintext blocks processed up to that point. To make each message unique, an initialization vector must be used in the first block.
Reference(s) used for this question:
HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, chapter 8: Cryptography (page 555).
and
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/One-time_pad http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Running_key_cipher http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cipher_block_chaining#Cipher-block_chaining_.28CBC.29
NEW QUESTION 23
What can be defined as a momentary low voltage?
- A. Spike
- B. Sag
- C. Fault
- D. Brownout
Answer: B
Explanation:
A sag is a momentary low voltage. A spike is a momentary high voltage. A fault is a momentary power out and a brownout is a prolonged power supply that is below normal voltage.
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw- Hill/Osborne, 2002, chapter 6: Physical security (page 299)
NEW QUESTION 24
......
P.S. 2passeasy now are offering 100% pass ensure SSCP dumps! All SSCP exam questions have been updated with correct answers: https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/SSCP/ (1074 New Questions)
